Quality professionals worldwide rely on tried-and-true tools to ensure process efficiency and problem-solving. The Basic Seven QC Tools, introduced by Kaoru Ishikawa, are fundamental techniques that empower teams to address issues systematically.
Here’s a quick guide to these tools, their purpose, uses, and benefits:
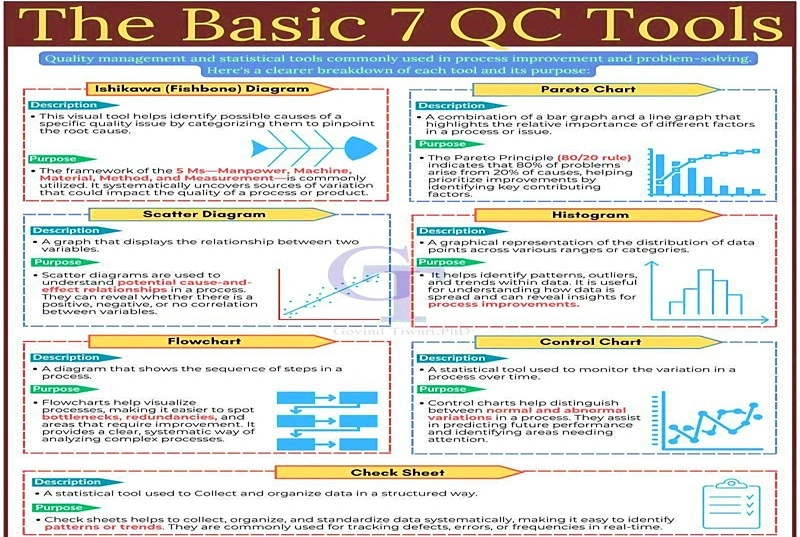
1. Fishbone Diagram (Cause-and-Effect Diagram)
Purpose: Identify potential causes of a problem and categorize them systematically.
Uses: Root cause analysis, brainstorming, and troubleshooting.
Benefits: Encourages team collaboration and helps visualize complex problems.
2. Pareto Chart
Purpose: Focus on the most significant factors contributing to a problem (80/20 rule).
Uses: Prioritize issues for resolution, analyze defects, or customer complaints.
Benefits: Highlights key areas to maximize improvement efforts efficiently.
3. Scatter Diagram
Purpose: Show relationships between two variables to identify correlations.
Uses: Analyzing cause-effect relationships, process improvements.
Benefits: Offers data-driven insights into trends and dependencies.
4. Histogram
Purpose: Visualize data distribution to understand variations.
Uses: Identify patterns, deviations, and trends in processes.
Benefits: Simplifies data interpretation for decision-making.
5. Flowchart
Purpose: Map processes step-by-step to identify inefficiencies or bottlenecks.
Uses: Process improvement, training, and communication.
Benefits: Enhances process transparency and promotes standardization.
6. Control Chart
Purpose: Monitor process stability and detect variations over time.
Uses: Statistical process control (SPC), quality monitoring.
Benefits: Prevents defects by identifying out-of-control conditions early.
7. Check Sheet
Purpose: Collect and organize data in a structured way.
Uses: Track defects, frequencies, or issues in real-time.
Benefits: Provides actionable data for analysis with minimal effort.
𝙒𝙝𝙮 𝙐𝙨𝙚 𝙏𝙝𝙚𝙨𝙚 𝙏𝙤𝙤𝙡𝙨?
• Simplicity: Easy to understand and implement.
• Versatility: Applicable across industries and processes.
• Effectiveness: Proven to improve problem-solving and quality.






